Using Spring security is very useful for our website development. It reduces risks from attacker, protect our data with cryptography.
So, understanding Spring security’s the mechanism is essential for us. In this article, we will cover knowledge about how Spring security works.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Spring security
- Mechanism of Spring security
- Some important note in Spring security
- Recap
Introduction to Spring security
Spring Security is a Java EE framework that focuses on providing both authentication and authorization to Java applications.
Some features are included into Spring Security:
- Comprehensive and extensible support for both Authentication and Authorization
- Protection against attacks like session fixation, clickjacking, cross site request forgery, etc
- Servlet API integration
- Optional integration with Spring Web MVC
Next, Spring security will contains some sub-modules:
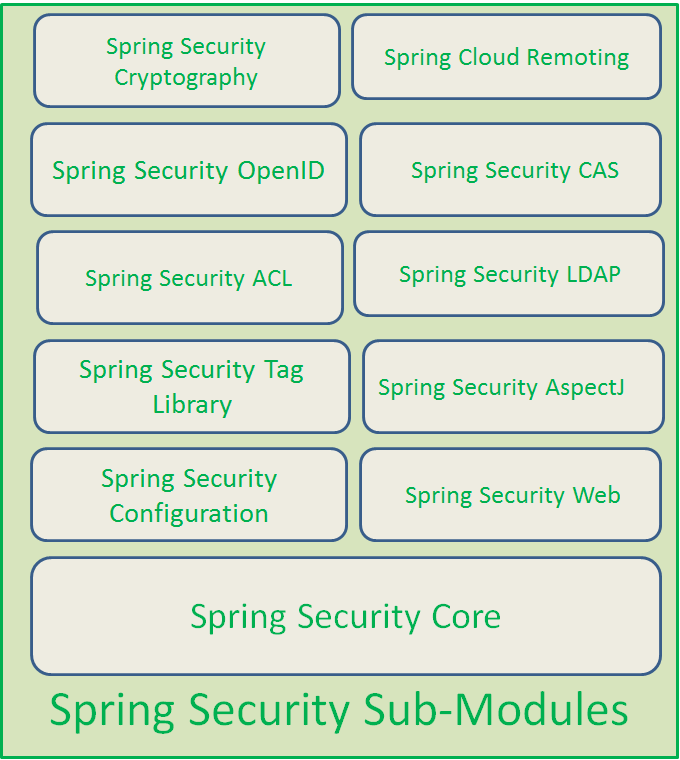
Mechanism of Spring security
Firstly, we will find out the general knowledge about Spring security. This information is referenced from this link.
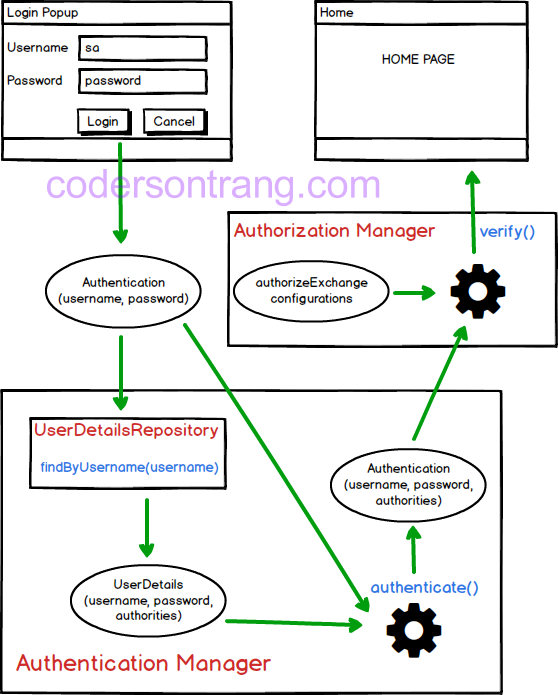
So, in Spring Security, we have two primary parts:
-
Authentication Manager
This part is responsible for authenticate user’s information that includes
usernameandpasswordwhich are typed in the login form. It will check whether username and password are valid or not.It will be used to answer a question Who are you?.
-
Authorization Manager
This part will be used to assign role for user after the above
authenticationstep passed. Based on their role, the system’s resource will be limited.It will be used to answer a question Which part will be limited to the user?.
We will explain all steps in the above image:
-
First of all, a user have to input a username and password in a login form. When a user completely finish this input stage, user will click to
Loginbutton, and username, password will be combined into an object ofAuthentication. -
Next, this
Authenticationobject will be sent to anauthenticate()method ofAuthentication Managerto check whether a username is valid or not.Based on
usernameinformation ofAuthenticationobject,Authentication Managerwill call theUserDetailsRepositoryto fetch all information that is stored in database system. All of this information is put into aUserDetailsobject, it will include username,password and authorities.Then, a password information in
UserDetailsobject will be compared to a password of theAuthenticationobject.If the above condition about password is invalid, user will come back to the login form. Otherwise, a new
Authenticationobject will be created, and it will contain not only username and password which is input from user, but also contain information about authorities which get from database system. -
The newly created
Authenticationwill be passed toAuthorization Managerto check user’s authorization.The user’s authorization will be checked based on a user’s role and the role that is needed from these resources. A user’s role is in the above
Authenticationobject.The role from resources will be configured in a
authorizeExchange()method. This comparison will be checked in averify()method ofAuthorization Manager. -
Finally, if the above comparison about authorization is valid, a user can access these resources. Otherwirse, a user will be received a notify that these resources can not access.
To go into the details of Spring security’s mechanism with Authetication, we will continue with the following image:
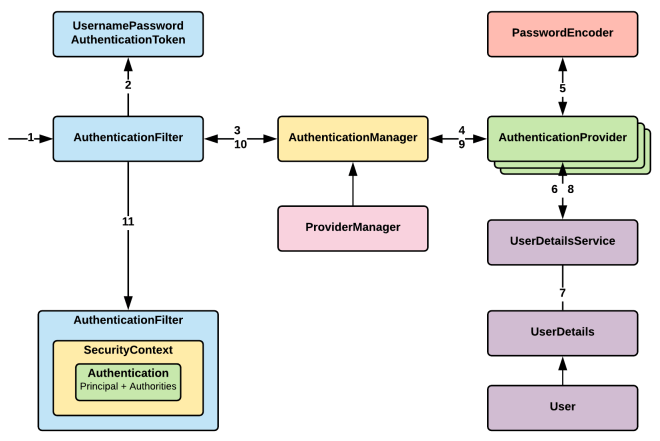
The explaination is referenced to the link.
After a user click a Login button to implement POST method in HTTP protocol, a request will reach the server, then, it is intercepted by the series of filters.
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter will handle the authentication request which extends from AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter.
For form based login, our login form must present two parameters to this filter: username and password.By default, this filter responds to the URL /login. But if we would like to have different parameters and different URL, then we have to override the attemptAuthentication() method.
public class CustomUsernamePasswordAuthFilter extends UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter {
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
// Your logic here
}
}
-
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
This filter has following abstract method which is implemented by
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.public abstract Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)This filter does the following operations.
-
First it checks for whether authentication is required or not based on our
HttpSecurityconfiguration. If authentication is not required, it simply invoke the next filter in the chain. -
If authentication requires, then it calls the
attemptAuthentication(request, response)which is implemented byUsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilterand this method returns theAuthenticationobject.
-
-
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
-
In
attemptAuthentication()method first it obtains the username & password from the request. -
Then it constructs the
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationTokenusing the below code. Which is nothing butAuthenticationobject.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);This
Authenticationobject will be as mentioned below.principal = username credentials = password authorities = null isAuthenticated = false -
So once it build the
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken/Authenticationobject, then it invokes theauthenticate()method ofAuthentication Manager. Means this filter delegates the job to theAuthenticationManager.this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
-
-
AuthenticationManager
ProviderManageris the implementation ofAuthenticationManagerand which has the following method.public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication); -
ProviderManager
ProviderManageriterates through all the provided/configuredAuthenticationProviders and delegate the actualAuthenticationjob toAuthenticationProviders.for(AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) { Authentication result = provider.authenticate(authentication); } -
AuthenticationProvider
-
There are many implementations for
AuthenticationProvider. One of the implementation isDAOAuthenticationProvider. Which extends from theAbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider. -
As mentioned above
AuthenticationManagerdelegates the job toAuthenticationProviderto authenticate the user. To thisAuthenticationProviderwe can pass/inject the following information.- UserDetailsService
- Salt
- PasswordEncoder
-
-
UserDetailsService
Which is responsible to load the actual user details which means
UserDetailsobject. We will have our custom implementation ofUserDetailsServiceto load or retrieve theUserDetailsobject either from internal memory or fromDatabase.public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService { @Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String userinput) throws UsernameNotFoundException { // Write a logic to retrieve the UserDetails from DB. } } -
PasswordEncoder
- We have multiple implementations of Password Encoder like
- MD4PasswordEncoder
- MD5PasswordEncoder
- ShaPasswordEncoder
- PlaintextPasswordEncoder
-
We can have our own implementation of password encoder.
public class PBKDF2PasswordEncoder implements PasswordEncoder { private static final int ITERATIONS = 10000; private static final int KEY_LENGTH = 256; private final static Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PBKDF2PasswordEncoder.class); @Override public String encodePassword(String rawPass, Object salt) { byte[] hashedPassword = null; if (rawPass != null && salt != null) { char[] passwordChars = rawPass.toCharArray(); byte[] saltBytes = (byte[]) salt; PBEKeySpec spec = new PBEKeySpec(passwordChars, saltBytes, ITERATIONS, KEY_LENGTH); try { SecretKeyFactory key = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("PBKDF2WithHmacSHA1"); hashedPassword = key.generateSecret(spec).getEncoded(); } catch (InvalidKeySpecException e) { LOG.error("Invalid key spec exception", e); throw new RuntimeException(e); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) { LOG.error("Not a valid algorithm", e); throw new RuntimeException(e); } return toBase64(hashedPassword); } return null; } @Override public boolean isPasswordValid(String encPass, String rawPass, Object salt) { byte[] saltBytes = fromBase64((String) salt); String encPasswd = encodePassword(rawPass,saltBytes); if(encPasswd != null && encPass != null) { return encPasswd.equals(encPass); } return false; } public byte[] fromBase64(String hex) throws IllegalArgumentException { return DatatypeConverter.parseBase64Binary(hex); } public String toBase64(byte[] array) { return DatatypeConverter.printBase64Binary(array); } }
- We have multiple implementations of Password Encoder like
-
Salt
Salt is a random Byte [] array. We can generate the salt as mentioned below.
public byte[] generateSalt() { byte[] salt = new byte[32]; Random random = new SecureRandom(); random.nextBytes(salt); return salt; }
Now finally AuthenticationProvider authenticate the user and build the Authentication object and return to the AuthenticationManager. Here i have mentioned some of the code blocks which helps you to understand the flow in detail.
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) {
UserDetails user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
}
This method retrieves the UserDetails object from DB using custom implementation of UserDetailsService.
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) {
UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
return loadedUser;
}
This method checks whether the provided password is valid or not.
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails user , UsernamePasswordAuthenticatonToken authentication) {
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
if(!passwordEncoder.isPasswordValid(userDetails.getPassword(),presentedPassword,salt)) {
logger.debug("Authentication failed: password does not match stored value");
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
Once password validated successfully, this method creates the Authentication object with Authorities and sets the isAuthenticated flag as true.
protected Authentication createSuccessAuthentication(Object principal,
Authentication authentication, UserDetails user) {
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken result =
new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(principal,authentication.getCredentials(),
authoritiesMapper.mapAuthorities(user.getAuthorities()));
return result;
}
-
createSuccessAuthentication()method creates the followingAuthenticationobject.principal = username credentials = password authorities = REGULAR_USER isAuthenticated = true -
AuthenticationProviderreturns theAuthenticationobject toAuthenticationManager. -
In the above mentioned
Authenticationprocess ifAuthenticationfails, then filter clears theSecuritycontext and invokes the failure-handler.protected void unsuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException failed) throws IOException, ServletException { SecurityContextHolder.clearContext(); failureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, failed); } -
If it successfully gets the
Authenticationobject then it does following things.- It stores the
Authenticationobject in theSecurityContextHolder. -
And it invokes the success-handler.
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult) throws IOException, ServletException { SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult); successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult); }
- It stores the
Some important note in Spring security
-
The difference between
loginPage()andloginProcessingURL()The method
loginPage("/login")instructs Spring security:- when authentication is required, redirect the browser to
/login. - we are in charge of rendering the login page when
/loginis requested - when authentication attempt fails, redirect the browser to
/login?error(since we have not specified otherwise) - we are in charge of rendering a failure page when
/login?erroris requested - when we successfully logout, redirect the browser to
/login?logout(since we have not specified otherwise) - we are in charge of rendering a logout confirmation page when /login?logout is requested
With method
loginProcessingURL("/login/process"):- this url is used to submit the username and password to
defaultSuccessUrl()- the landing page after a successful login. - tells Spring security to process the submitted credentials when sent the specified path and, by default, redirect user back to the page user came from. It will not pass the request to Spring MVC and controller.
- when authentication is required, redirect the browser to
-
Explain about
customlogin.html<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head th:include="layout :: head(title=~{::title},links=~{})"> <title>Please Login</title> </head> <body th:include="layout :: body" th:with="content=~{::content}"> <div th:fragment="content"> <form name="f" th:action="@{/login}" method="post"> <!--(1)--> <fieldset> <legend>Please Login</legend> <div th:if="${param.error}" class="alert alert-error"> <!--(2)--> Invalid username and password. </div> <div th:if="${param.logout}" class="alert alert-success"> <!--(3)--> You have been logged out. </div> <label for="username">Username</label> <input type="text" id="username" name="username"/> <!--(4)--> <label for="password">Password</label> <input type="password" id="password" name="password"/> <!--(5)--> <div class="form-actions"> <button type="submit" class="btn">Log in</button> </div> </fieldset> </form> </div> </body> </html>- (1) - The URL we submit our username and password to is the same URL as our login form (i.e. /login), but a POST instead of a GET.
- (2) - When authentication fails, the browser is redirected to /login?error so we can display an error message by detecting if the parameter error is non-null.
- (3) - When we are successfully logged out, the browser is redirected to /login?logout so we can display an logout success message by detecting if the parameter logout is non-null.
- (4) - The username should be present on the HTTP parameter username
- (5) - The password should be present on the HTTP parameter password
-
The meaning of some methods in
configure()method ofWebSecurityConfigurerAdapterclassloginPage("/login"): The url which points to a ```@RequestMapping which returns the login form.loginProcessingUrl("/login"): The url which triggers theUsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter. It is equivalent to build a POST processing controller method.defaultSuccessUrl("/user"): The default page where the user will be redirected after providing a valid user credentials.failureUrl("/login?error=true"): The url where user will be redirected in case of trying to login with invalid credentials.
-
Why to use POST method with URL is “/login” as parameter of
loginPage("/login")in login.html, it can not be called.@RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = RequestMethod.POST) public ModelAndView doLogin() { System.out.println("***LOGIN_POST***"); return new ModelAndView("users/home"); }So, the above code won’t be reached.
When mapping a post to
/loginuri, theUsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilterwill perform it’sdoFilter()method to catch the user provided credentials, build aUsernamePasswordAuthenticationTokenand delegate it to theAuthenticationManager, where thisAuthenticationwill be executed in the matchingAuthenticationProvider. -
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilterclassIt is extended from
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilterclass and some other interfaces.When the url in
loginProcessingURL("/login")is implemented, this class will process an authentication form submission. And login form must present two parameters to this filter: a username and password.So, this class’s responsibility is to get username and password from login form.
We can refer this link to read about some methods of this class.
-
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationTokenclassIt is extended from the abstract class
AbstractAuthenticationTokenand implemented interfaces such asSerializable,Principal,Authentication,CredentialsContainer.An
Authenticationimplementation that is designed for simple presentation of a username and password.In the
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationTokenclass, we can see that it has two constructor:UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(java.lang.Object principal, java.lang.Object credentials); UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(java.lang.Object principal, java.lang.Object credentials, java.util.Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities);In the above two constructors, we have to pass
principalandcredentialsobjects, or authorities of user.And this class also support some method to make an action with
principalandcredentials.void eraseCredentials(); Object getCredentials(); Object getPrincipal(); void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated);So, we have two questions:
- What is principal and credential?
- When/How are two object - principal and credentials created?
To end up this class, we have conclusion -
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationTokenclass will contain all information aboutprincipal(the principal can be username),credentials(the credentials are a password) andauthorities. -
AuthenticationManagerclassIt is an interface class, has derived class that is
ProviderManagerclass.This class has only one method:
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;authenticate()method will attempts to authenticate the passedAuthenticationobject, returning a fully populatedAuthenticationobject (including granted authorities) if successful. -
AuthenticationProviderclassIt is also interface class and some classes implementing this interface are
AbstractJaasAuthenticationProvider, AbstractLdapAuthenticationProvider, AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider, ActiveDirectoryLdapAuthenticationProvider, AnonymousAuthenticationProvider, AuthenticationManagerBeanDefinitionParser.NullAuthenticationProvider, CasAuthenticationProvider, DaoAuthenticationProvider, DefaultJaasAuthenticationProvider, JaasAuthenticationProvider, LdapAuthenticationProvider, OpenIDAuthenticationProvider, PreAuthenticatedAuthenticationProvider, RememberMeAuthenticationProvider, RemoteAuthenticationProvider, RunAsImplAuthenticationProvider, TestingAuthenticationProvider.It also provides a method for performing authentication with the same contracts as
AuthenticationManager.authenticate(Authentication).Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException; -
ProviderManagerclassIt is extended from Object class and implemented from some interfaces such as
AuthenticationManager, …We can see some constructors to know about it.
ProviderManager(List<AuthenticationProvider> providers); ProviderManager(List<AuthenticationProvider> providers, AuthenticationManager parent);So,
ProviderManagerwill manage the list ofAuthenticationProvider.And it also provides an
authenticate()method that do the same meaning with anauthenticate()method ofAuthenticationManagerandAuthenticationProviderclasses.public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;This method will attempt to authenticate the passed
Authenticationobject.The list of
AuthenticationProviders will be successively tried until anAuthenticationProviderindicates it is capable of authenticating the type ofAuthenticationobject passed.Authenticationwill then be attempted with thatAuthenticationProvider.If more than one
AuthenticationProvidersupports the passedAuthenticationobject, the first one able to successfully authenticate theAuthenticationobject determines the result, overriding any possibleAuthenticationExceptionthrown by earlier supportingAuthenticationProviders. On successful authentication, no subsequentAuthenticationProviders will be tried. If authentication was not successful by any supportingAuthenticationProviderthe last thrownAuthenticationExceptionwill be rethrown. -
Explain about
principalandcredentialsAuthentication represents the process by which the identify of a subject is verified, , and must be performed in a secure fashion; otherwise a perpetrator may impersonate others to gain access to a system. Authentication typically involves the subject demonstrating some form of evidence to prove its identity.
Once authenticated, a Subject is populated with associated identities, or Principals (of type java.security.Principal). A Subject may have many Principals. For example, a person may have a name Principal (“John Doe”) and an SSN Principal (“123-45-6789”), which distinguish it from other Subjects.
In addition to associated Principals, a Subject may own security-related attributes, which are referred to as credentials. A credential may contain information used to authenticate the subject to new services. Such credentials include passwords, Kerberos tickets, and public key certificates. Credentials might also contain data that enables the subject to perform certain activities. Cryptographic keys, for example, represent credentials that enable the subject to sign or encrypt data. Public and private credential classes are not part of the core Java SE API. Any class, therefore, can represent a credential.
Recap
- Understanding about mechanism of Spring Security will help us to customize the authentication and authorization to follow our thought.
Refer:
Spring security architecture
https://spring.io/guides/topicals/spring-security-architecture/
https://blog.imaginea.com/spring-security-architecture-part-1/
https://www.blog.labouardy.com/spring-security-authentication/
https://www.dineshonjava.com/spring-security-take-baby-step-to-secure/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spring_Security
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/53140629/spring-security-loginpage-vs-loginprocessingurl
Creating the custom login page
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/current/guides/html5/form-javaconfig.html
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-security-login
Spring security overview
Send information username and password from form-submit to Server
SecurityContext and SecurityContextHolder https://www.javacodegeeks.com/2018/02/securitycontext-securitycontextholder-spring-security.html
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/security/jgss/tutorials/glossary.html
AuthenticationProvider
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-security-authentication-provider