When we want to change the position of element in css, we have to use position property. It make us easy to set a new position of element to follow many conditions such as parent element, browser window, …
So, in this article, we will find out some basic information about position property in CSS.
Table of contents
- Introduction to position property
- Properties accompany with position property
- Static value
- Relative value
- Absolute value
- Fixed value
- Wrapping up
Introduction to position property
According to w3schools.com, we have:
The position property specifies the type of positioning method used for an element (static, relative, absolute, fixed, or sticky).
The below image and table describe some values of position property:
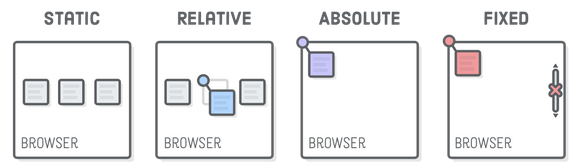
| value | Description |
|---|---|
| static | Default value. Elements render in order, as they appear in the document flow |
| absolute | The element is positioned relative to its first positioned (not static) ancestor element |
| fixed | The element is positioned relative to the browser window |
| relative | The element is positioned relative to its normal position, so “left: 20px” adds 20 pixels to the element’s LEFT position |
| sticky | The element is positioned based on the user’s scroll position |
Properties accompany with position property
Before, go deeper into some properties top, right, bottom, and left, we will have to understand about coordinate system in CSS.
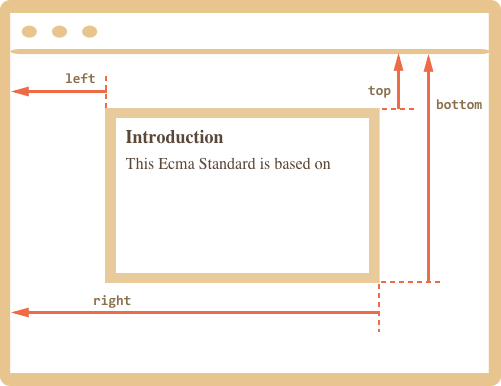
- top - Y-coordinate for the top element edge.
- left - X-coordinate for the left element edge.
- right - X-coordinate for the right element edge.
- bottom - Y-coordinate for the bottom element edge.
So, an origin point in coordinate system is the most top-left with top = 0, left = 0.
- top: if its value > 0, element will go from up to down; if not, element go from down to up.
- bottom: if its value > 0, element will go from down to up; it not, element will go from up to down.
- right: if its value > 0, element will run from right to left; it not, element will run from left to right.
- left: if its value > 0, element will run from left to right; if not, element will run from right to left.
To understand about values of top, right, bottom, and left properties, we have an image:

When we have a parent element that has position: relative, we want to align a child element with position: absolute to follow a parent’s position. We will have some conditions:
- If
top = 0andleft = 0, a child element will at the most top-left. - If
top = 0andright = 0, a child element will at the most top-right. - If
bottom = 0andleft = 0, a child element will at the most bottom-left. - If
bottom = 0andright = 0, a child element will at the most bottom-right. - If
top = 0,right = 0,bottom = 0, andleft = 0, a child element will expand whole a parent element with a condition: do not set values forwidth,heightproperties of a child element. - If
left = 0,right = 0and we do not set value forwidthproperty of a child element, a child element haswidthproperty that is equal to 100% of a parent element’s width. - If
top = 0,bottom = 0and we do not set value forheightproperty of a child element, a child element hasheightproperty that is equal to 100% of parent element’s height. - The other properties such as
margin,background, … can be used to go withpositionproperty.
Static value
The element is positioned according to the normal flow of the document.
The top, right, bottom, left and z-index properties have no effect.
This is the default value.
Relative value
This value will help us to change the position of element without influencing the other element. It do not push the other element to a new position.
<img src="../img/front-end/relative-beach.jpeg" alt="">
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Quod atque aspernatur nostrum. Porro aspernatur qui sit saepe placeat eum quae impedit ut atque cupiditate eligendi numquam nisi, quasi repudiandae nemo!</p>
img {
position: relative;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
outline: 2px solid #000;
max-width: 100px;
}
We have a result:

So, we have:
- The element is positioned according to the normal flow of the document, and then offset relative to itself based on the values of
top,right,bottomandleft. - The offset does not effect the position of any other elements, thus, the space given for the element in the page layout is the same as if the position were static.
- This value creates a new
stacking contextwhen the value ofz-indexis notauo. Its effect ontable-*-group,table-row,table-column,table-cell, andtable-captionelements is undefined.
Absolute value
This value is usually used with a case: a parent element has position: relative, a child element has position: absolute.
So, the position of child element will set based on a parent element.
<div class="parent-element">
<div class="child-element"></div>
</div>
.parent-element {
position: relative;
height: 250px;
background-color: #00aefd;
margin: 20px;
}
.child-element {
position: absolute;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
top: 100px;
left: 10px;
background-color: #e74c3c;
}
The result will be:

So, we will have:
- The element is removed from the normal document flow, and no space is created for the element in the page layout.
- It is positioned relative to its closet positioned ancestor, if any; otherwise, it is placed relative to the initial containing block. Thus, its final position is determined by the values of
top,right,bottom, andleft. - It creates a new
stacking contextwhen the value ofz-indexis notauto. The margins of absolutely positioned boxes do not collapse with other margins.
Fixed value
This value is usually used for navigation bar when scrolling content in browser.
<div class="content">
<ul>
<li><a href="">home</a></li>
<li><a href="">about</a></li>
<li><a href="">contact</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
body {
height: 200vh;
}
.content {
width: 100%;
height: 400px;
background-color: #00aefd;
}
ul {
padding: 10px;
background-color: #ccc;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
}
ul li {
list-style-type: none;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
color: #00aefd;
font-size: 20px;
text-transform: uppercase;
font-weight: bold;
}
We will have a result for this case.

So, we have:
- The element is removed from the normal document flow, and no space is created for the element in the page layout.
- It is positioned relative to the initial containing block established by the viewport, except when one of its ancestors has a
transform,perspective, orfilterproperty set to something other thannone. Its final position is determined by the values oftop,right,bottom, andleft. - It creates a new
stacking context.
Wrapping up
- When an element is set the
positionproperty withrelative, it has two functions:- First, it is a parent of the other element when child element has
positionproperty withabsolute. - Second, it will change the origin position to follow the values of
top,right,bottom,left.
- First, it is a parent of the other element when child element has
- Usually, using the
stickyvalue ofpositionproperty is for navigation menu.
Refer:
https://www.w3schools.com/cssref/playit.asp?filename=playcss_position&preval=fixed
https://kipalog.com/posts/Tim-hieu-thuoc-tinh-position-trong-CSS
Coordinate system in CSS